How To Change Index Values In Pandas Dataframe
Pandas DataFrame is nothing but an in-memory representation of an excel sheet via Python programming language. An index object is an immutable array. Indexing allows us to access a row or column using the label.
Pandas DataFrame is a composition that contains two-dimensional data and its correlated labels. The DataFrame is a 2D labeled data structure with columns of a potentially different type. DataFrames are famously used in data science, machine learning, scientific computing, and many other data-intensive fields.
Pandas set index
Pandas set_index() method is used to set the list, series, or dataframe as an index of the dataframe. It takes keys, drop, append, inplace, andverify_integrityas parameters and returns the data frame with index using one or more existing columns.
To set the DataFrame index using existing columns or array in Pandas, use the set_index() method. The set_index() function sets the DataFrame index using existing columns. The index can replace the existing index or expand on it.
Syntax
DataFrame.set_index(keys, drop=True, append=False, inplace=False, verify_integrity=False)
Set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns. By default, it yields the new object.
Parameters
- keys:Column name or list of a column name.
- drop: It's aBoolean value that falls the column used for the index if True.
- append:It appends the column to the existing index column if True.
- inplace: It makes the changes in the DataFrame if True.
- verify_integrity: It checks the new index column for duplicates if True.
Example
We will use Real data that can be found on the following Google Docs link.
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1zeeZQzFoHE2j_ZrqDkVJK9eF7OH1yvg75c8S-aBcxaU/edit#gid=0
Pandas DataFrames are data structures that contain:
- Data organized intotwo dimensions, which are rows and columns.
- Labels that coincide with therows andcolumns
Now, open the Jupyter Notebook and import the Pandas Library first.
Write the following code inside the first cell in Jupyter Notebook.
import pandas as pd
Run the cell by hittingCtrl + Enter.
Okay, now we will use theread_csv()function of the DataFrame data structure in Pandas. So write the following code in the next cell.
data = pd.read_csv('data.csv', skiprows=4) data We have used the read_csv()function and skipped the first four rows, and then display the remaining rows. Run the cell and see the output. It will show the first 30 rows and the last 30 rows if there are so many rows.
In our data file, there are above 29,000 rows. That is why we can see the first and last 30 rows.
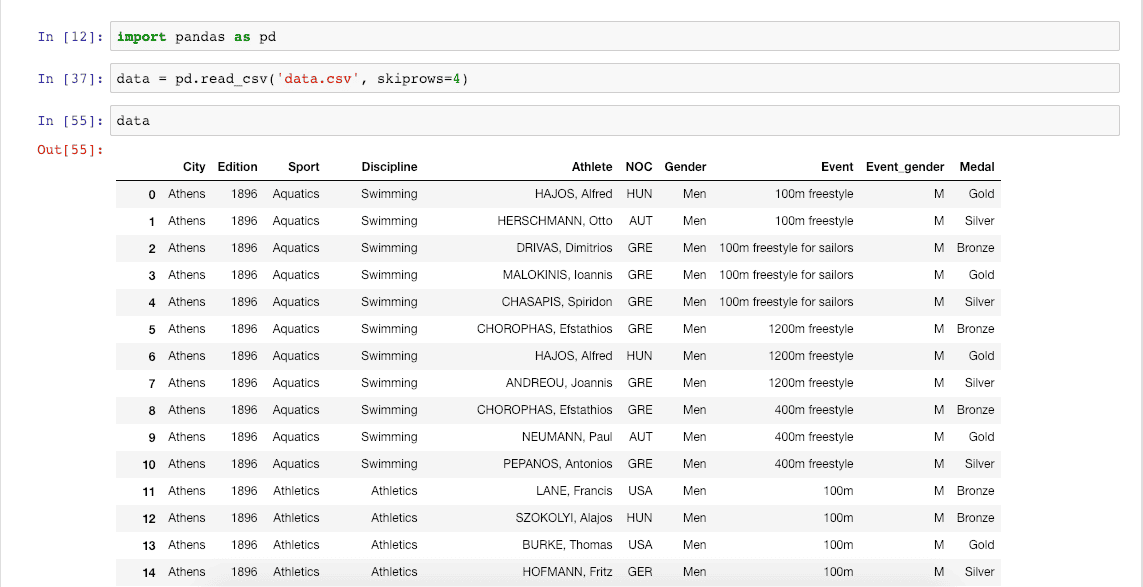
If you get the above output, then you have successfully imported the data.
The first row holds the column labels (City, Edition, Sport, Discipline, Athlete, NOC, Gender, Event, Event_gender, and Medal). The first column holds the row labels (0, 1, 2, and so on). All other cells are filled with data values.
There are several ways that you can create the Pandas DataFrame. In most cases, you will use the DataFrame constructor and fill out the data, labels, and other information. Sometimes, you will import the data from a CSV or Excel file. Then, you can pass the data as the two-dimensional list, tuple, or NumPy array. You can also pass it as the dictionary or Pandas Series instance or as one of many other data types not covered in this example.
Now, let's see the type of index object.
Okay, in the next cell, type the following code to see the type of index object.
type(data.index)
See the below output.

Here you can see that the index has its type.
Remember that the index data is immutable, and we can not change that in any circumstances.
Pandas DataFrame set_index() Example
Now, we will set an index for the Python DataFrame using theset_index() method.
There are two ways to set the DataFrame index.
- Use the parameterinplace=Trueto set the current DataFrame index.
- Assign the newly created DataFrame index to a variable and use it further to use the Indexed result.
Let's see the first way. But, first, let's choose the Athleteas an index and set that column as an index.
Write the following code in the next cell and see the output.
data.set_index('Athlete',inplace=True) Run the cell and now display the DataFrame using the following code in the next cell.
data
We can see that in the output that the DataFrame is indexed based on the Athlete Names.

Here, in the code, we have passed theinplace=Trueas a parameter, which means assigning the Athleteindex to the current DataFrame.
Pandas DataFrames can sometimes be very large, making it absurd to look at all the rows at once. You can use.head() to show the first few elements and .tail() to show the last few elements.
Each column of the Pandas DataFrame is an instance of Pandas Series, a structure that contains one-dimensional data and its labels. Thus, you can get a single element of a Series object the same way you would with a dictionary using its label as the key.
The attributes .ndim, .shape, and .size return the number of dimensions, the number of data values across each dimension, and a total number of data values, respectively.
Reset Index in Pandas DataFrame
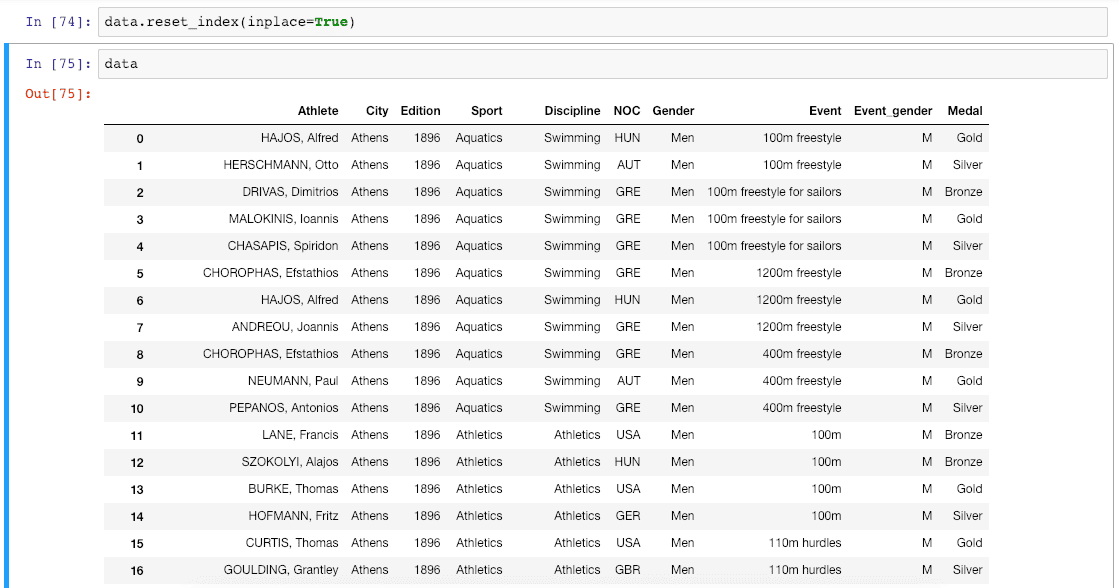
Pandas reset_index() method resets an index of a Data Frame. reset_index() method sets a list of integers ranging from 0 to length of data as an index. We can use thereset_index()function to reset the index. Let's see the following code.
data.reset_index(inplace=True) data
See the output below.
Now, see the second way to use the set_index() method.
Write the following code in the next cell.
indexedData = data.set_index('Athlete') indexedData See the below output.

Here, we can see that we have not passed thesecondparameter, and also, we have saved the data to the other variable and display that data into the Jupyter Notebook.
So, in this tutorial, we have seen both the methods to use any column as an index and also see how we can reset that index using the reset_index() method.
Other Examples of Python Set Index
Python is an extraordinary language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric python packages.
Python's Pandas is one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much more comfortable.
Pandas set_index() is the method to set a List, Series, or Data frame as an index of a DataFrame.
Index column can be set while making the data frame too. But sometimes, the data frame is made out of two or more data frames, and hence later, the index can be changed using the set_index() method.
>>> df = pd . DataFrame ({ 'month' : [ 1 , 4 , 7 , 10 ], ... 'year' : [ 2012 , 2014 , 2013 , 2014 ], ... 'sale' : [ 55 , 40 , 84 , 31 ]}) >>> df month year sale 0 1 2012 55 1 4 2014 40 2 7 2013 84 3 10 2014 31
Set the index to become the 'month' column:
>>> df . set_index ( 'month' ) year sale month 1 2012 55 4 2014 40 7 2013 84 10 2014 31
Create the MultiIndex using columns' year' and 'month':
>>> df . set_index ([ 'year' , 'month' ]) sale year month 2012 1 55 2014 4 40 2013 7 84 2014 10 31
Create the MultiIndex using an Index and a column:
>>> df . set_index ([ pd . Index ([ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]), 'year' ]) month sale year 1 2012 1 55 2 2014 4 40 3 2013 7 84 4 2014 10 31
Create a MultiIndex using two Series:
>>> s = pd . Series ([ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]) >>> df . set_index ([ s , s ** 2 ]) month year sale 1 1 1 2012 55 2 4 4 2014 40 3 9 7 2013 84 4 16 10 2014 31
Python Dataframe set_index not setting
Let's say you have a data frame and set the index to the column 'Timestamp'.
Currently, the index is just a row number. For example, the Timestamp's format is 2019-10-02 15:42:00.
You need to write the following code to set_index.
df.set_index('Timestamp', inplace=True, drop=True) You need to either specify inplace=True or assign the result to the variable.
Convert index of pandas DataFrame into column
You can access a column in a Pandas DataFrame the same way you would get a value from a dictionary.
Let's figure out how to convert an index of the data frame to a column.
From our example, let's set the index to the column sales.
For that, we need to write the following code snippet.
df['sales'] = df.index
Or, we can reset_index().
df.reset_index(level=0, inplace=True)
Pandas set index to multiple columns.
In this example, two columns will be made as index columns.
The drop parameter is used to Drop the column, and the append parameter is used to append the passed columns to the already existing index column.
df.set_index(["Month", "Year"], inplace = True, append = True, drop = False)
With df.reset_index(level=df.index.names, inplace=True) one can convert a given whole multiindex into columns.
You can change the index as explained already using the set_index() method.
You don't need to swap rows with columns manually; there is a Pandas transpose() method in pandas that does it for you.
How to assign multi-index in Pandas DataFrame
You can use the set_index() function so that multiple columns can be assigned as multi-index. By specifying a list of column names in the first argument keys, multiple columns are assigned as multi-index.
Let's say we have this data: people.csv
Okay, let's create a DataFrame from the CSV file.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv('people.csv') df = pd.DataFrame(data) print(df.head(10)) Output
Name Sex Age Height Weight 0 Alex M 41 74 170 1 Bert M 42 68 166 2 Carl M 32 70 155 3 Dave M 39 72 167 4 Elly F 30 66 124 5 Fran F 33 66 115 6 Gwen F 26 64 121 7 Hank M 30 71 158 8 Ivan M 53 72 175 9 Jake M 32 69 143
Okay, now let's set two columns as an index. See the following code.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv('people.csv') df = pd.DataFrame(data) df10 = df.head(10) df_mul_index = df10.set_index(['Sex', 'Age']) print(df_mul_index) Output
Name Height Weight Sex Age M 41 Alex 74 170 42 Bert 68 166 32 Carl 70 155 39 Dave 72 167 F 30 Elly 66 124 33 Fran 66 115 26 Gwen 64 121 M 30 Hank 71 158 53 Ivan 72 175 32 Jake 69 143
From the output, you can see that we have assigned a multi-index.
Sorting with the sort_index() function makes it displayed neatly.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv('people.csv') df = pd.DataFrame(data) df10 = df.head(10) df_mul_index = df10.set_index(['Sex', 'Age']) df_mul_index.sort_index(inplace=True) print(df_mul_index) Output
Name Height Weight Sex Age F 26 Gwen 64 121 30 Elly 66 124 33 Fran 66 115 M 30 Hank 71 158 32 Carl 70 155 32 Jake 69 143 39 Dave 72 167 41 Alex 74 170 42 Bert 68 166 53 Ivan 72 175
Now, it's neat and clean.
Pandas set index: change index to another column.
If you set another column with set_index(), the original index will be deleted. If you want to keep the original index as a column, use reset_index() to reassign the index to a sequential number starting from 0. See the code.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv('people.csv') df = pd.DataFrame(data) df10 = df.head(10) df_mul_index = df10.set_index(['Sex', 'Age']) df_re_index = df_mul_index.reset_index() print(df_re_index) Output
Sex Age Name Height Weight 0 M 41 Alex 74 170 1 M 42 Bert 68 166 2 M 32 Carl 70 155 3 M 39 Dave 72 167 4 F 30 Elly 66 124 5 F 33 Fran 66 115 6 F 26 Gwen 64 121 7 M 30 Hank 71 158 8 M 53 Ivan 72 175 9 M 32 Jake 69 143
Select rows and elements using index
You can select rows and elements by the name index using loc[].
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv('people.csv') df = pd.DataFrame(data) df10 = df.head(10) df_index = df10.set_index(['Name']) daloc = df_index.loc['Gwen'] print(daloc) Output
Sex F Age 26 Height 64 Weight 121 Name: Gwen, dtype: object
Finally, the Pandas Set Index Example is over.
Recommended Posts
Pandas boolean_indexing()
Pandas sort_values()
Pandas value_counts()
Pandas iloc[]
Pandas filter()
How To Change Index Values In Pandas Dataframe
Source: https://appdividend.com/2019/01/26/pandas-set-index-example-python-set_index-tutorial/
Posted by: nollexperkee.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Change Index Values In Pandas Dataframe"
Post a Comment